[풀이]백준 풀이(XI/16928 등 )
문제풀이
Maaaaaaaze(16985, BFS, 시뮬레이션, 경우의 수)
- 5x5 2차원 배열 5개를 쌓는다 (5x5x5 3차원 배열)
- 회전 가능
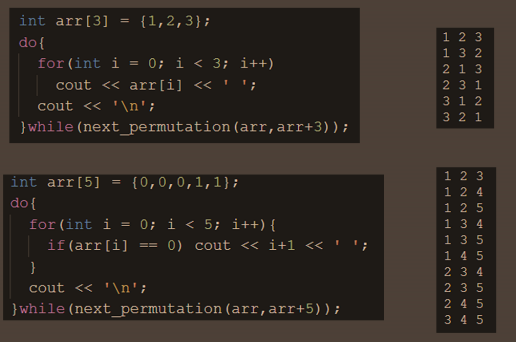
- 3차원 배열이므로 tuple 사용
- 쌓는 순서 변경가능 -> next_permutation 사용
따라서
- 입력을 받는다
- 큐브를 생성한다
- 회전
- 쌓는 순서 변경
- bfs를 실행한다.
순으로 진행했다.
회전
rotation함수를 생성해서 회전을 구현했으나 괴랄한 for문이 생성되었다.
확인한 결과, rotation을 계속 실행하는 건 매우 비효율적이므로 dp처럼 rotation을 한 번씩 실행해서 모두 저장해놓는 것이 빠르게 실행하는데 도움이 된다.
아래 코드 틀린답입니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <tuple>
#define INF 987654321
using namespace std;
vector<int> floatIndex;
int tempmaze[5][5][5];
int realMaze[5][5][5];
bool check[5][5][5];
int dz[6] = { 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, -1, };
int dy[6] = { 0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0 };
int dx[6] = { 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0 };
int Answer=INF;
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
tempmaze[i][j][k] = 0;
realMaze[i][j][k] = 0;
check[i][j][k] = false;
}
}
}
}
bool isInside(int x, int y, int z) {
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && z >= 0 && x < 5 && y < 5 && z < 5) return true;
else return false;
}
void saveMaze() {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < 5; y++) {
for (int z = 0; z < 5; z++) {
tempmaze[x][y][z] = realMaze[x][y][z];
}
}
}
}
void loadMaze() {
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < 5; y++) {
for (int z = 0; z < 5; z++) {
realMaze[x][y][z] = tempmaze[x][y][z];
}
}
}
}
//rotation = right, 3rotation = left;
void rotation(int x) {
//(x,y) = (y, 4-x)
for (int y = 0; y < 5; y++) {
for (int z = 0; z < 5; z++) {
//회전... .이렇게 해도 되나?
int temp = realMaze[x][z][4 - y];
realMaze[x][y][z] = temp;
}
}
}
void bfs(int sx, int sy, int sz) {
//회전 1. (중복발생)
for (int idx1 = 0; idx1 < 5; idx1++) {
for (int idx2 = 0; idx2 < 5; idx1++) {
for (int idx3 = 0; idx3 < 5; idx1++) {
for (int idx4 = 0; idx4 < 5; idx1++) {
for (int idx5 = 0; idx5 < 5; idx1++) {
//cout << "idx5=" << idx5 << "\n";
saveMaze();
for (int a = 0; a < idx1; a++) {
rotation(0);
}
for (int a = 0; a < idx2; a++) {
rotation(1);
}
for (int a = 0; a < idx3; a++) {
rotation(2);
}
for (int a = 0; a < idx4; a++) {
rotation(3);
}
for (int a = 0; a < idx5; a++) {
rotation(4);
}
queue<tuple<int, int, int>> q;
q.push(tuple<int, int, int>(sx, sy, sz));
//move, bfs
int Answer_candidate = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
tuple<int, int, int> t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
int nx = get<0>(t) + dx[i];
int ny = get<1>(t) + dy[i];
int nz = get<2>(t) + dz[i];
if (realMaze[nx][ny][nz] == 1 && isInside(nx, ny, nz) && !check[nx][ny][nz])
{
check[nx][ny][nz] = true;
q.push(tuple<int, int, int>(nx, ny, nz));
Answer_candidate++;
}
}
}
Answer = min(Answer, Answer_candidate);
//realMaze 원복
loadMaze();
}
}
}
}
}
//이동
//판 위 아래 변경
}
void makeCube() {
int x = 0, y = 0, z = 0;
do {
for (x = 0; x < 5; x++) {
//cout << "realMaze Index = x, y, z" << x << "," << y << "," << z;
//cout << " tempMaze Index = x, y, z" << floatIndex[x] << "," << y << "," << z;
for (y = 0; y < 5; y++) {
for (z = 0; z < 5; z++) {
realMaze[x][y][z] = tempmaze[floatIndex[x]][y][z];
}
}
//cout << endl;
}
bfs(0, 0, 0);
} while (next_permutation(floatIndex.begin(), floatIndex.end()));
}
int main() {
//초기화
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
init();
//입력
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
floatIndex.push_back(i);
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
cin >> tempmaze[i][j][k];
}
}
}
makeCube();
if (!check[4][4][4]) Answer = -1;
cout << Answer;
}
풀이 (정답)
- 일단 큐브를 만들고 나서야 BFS로 탈출하는데 걸리는 시간을 구할 수 있다.
- 판을 쌓는 방법 5!
- 큐브를 회전시키는 방법 4^5
- 약 122,880개의 큐브에서 (0,0,0) to (4,4,4) bfs
- BFS는 최대 125개의 칸을 거치고 6개의 방향을 고려하면
- 약 92,160,000개으 경우의 수가 나온다.
입력부분과 bfs부분에서 부족한게 있었다.. 나머지는 거의 동일했으니 이제 고지에 올라가자 ㅠㅠ,,,,
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <tuple>
#define INF 987654321
using namespace std;
//board[dir][i][j][k]: i번째 판을 시계방향으로 dir번 돌렸을 때 (j,k)의 값
int board[4][5][5][5];
int maze[5][5][5];
int dist[5][5][5];
int dx[6] = {1,0,0,0,0,-1};
int dy[6] = {0,1,-1,0,0,0};
int dz[6] = {0,0,0,1,-1,0};
int Answer = INF;
void init(){
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
for(int j=0; j<5; j++){
for(int k=0; k<5; k++){
dist[i][j][k] = -1;
}
}
}
}
bool isInside(int x, int y, int z) {
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && z >= 0 && x < 5 && y < 5 && z < 5) return true;
else return false;
}
int solve(int sx, int sy, int sz){
if(maze[0][0][0] == 0 || maze[4][4][4] == 0) return INF;
init();
queue<tuple<int,int,int>> q;
q.push(tuple<int, int, int>(sx,sy,sz));
dist[sx][sy][sz] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
tuple<int, int, int> t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int dir=0; dir<6; dir++){
int nx,ny,nz;
tie(nx,ny,nz) = t;
nx += dx[dir];
ny += dy[dir];
nz += dz[dir];
if(!isInside(nx,ny,nz)) continue;
//다음 미로가 막혀있거나, 방문한 적이 있으면 PASS
if(maze[nx][ny][nz] == 0 || dist[nx][ny][nz] != -1) continue;
//마지막칸에 도달했으면 끝
int xtmp, ytmp, ztmp;
tie(xtmp,ytmp,ztmp) = t;
if(nx == 4 && ny == 4 && nz==4) return dist[xtmp][ytmp][ztmp];
dist[nx][ny][nz] = dist[xtmp][ytmp][ztmp]+1;
q.push(tuple<int, int, int>(nx,ny,nz));
}
}
return INF;
}
int main(){
//flush and speed
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
//회전같긴한데,,,
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
//원래형태 입력
scanf("%d",&board[0][i][j][k]);
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
//1회전 입력
board[1][i][j][k] = board[0][i][4-k][j];
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
//1회전 + 1회전 입력
board[2][i][j][k] = board[1][i][4-k][j];
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
//2회전 +1회전 입력
board[3][i][j][k] = board[2][i][4-k][j];
}
int order[5] = {0,1,2,3,4}; // 판을 쌓는 순서
do{
//4^5
for(int i=0; i<1024; i++){
int tmp = i; //5개의 판의 dir을 정해주는 변수
for(int j=0; j<5; j++){
int dir = tmp%4;
tmp /=4;
for(int k=0; k<5; k++){
for(int l=0; l<5; l++){
maze[j][k][l] = board[dir][order[j]][k][l];
}
}
}
Answer = min(Answer, solve(0,0,0));
}
}while(next_permutation(order, order+5));
if(Answer == INF) cout << -1;
else cout << Answer+1;
}
2146(다리만들기, bfs)
- 2차원 배열이 있다.
- 모든 섬을 찾아낸 뒤, 모든 육지에서 bfs를 실행하여 min값을 출력하면 된다.
58프로에서.. 계속틀린다… 다시짜야하나……
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#define INF 987654321
using namespace std;
int a, groupIdx=INF, z=0;
int map[100][100];
int dist[100][100];
bool check[100][100];
///////////////////////////////
int Answer = INF;
int group[100];
bool check2[100][100];
int dist2[100][100];
int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1};
int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0};
void init(){
for(int i=0; i<a; i++){
for(int j=0; j<a; j++){
map[i][j]=0;
dist[i][j]=0;
check[i][j]=false;
check2[i][j]=false;
}
}
}
bool isInside(int x, int y){
if(x>=0 && y>=0 && x<a && y<a) return true;
else return false;
}
//문제 dist값이 갱신이 안돼
void bfs(int sx, int sy){
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(sx,sy));
//방문체크
dist[sx][sy]=groupIdx;
check[sx][sy]=true;
while(!q.empty()){
pair<int,int> n;
n = q.front();
q.pop();
int nx, ny;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
nx = n.first + dx[i];
ny = n.second+ dy[i];
//온적이 없고 범위안이고 갈 수 있으면
if(dist[nx][ny]== 0 && isInside(nx,ny) && !check[nx][ny] && map[nx][ny]==1)
{
//그룹화 && 큐에 삽입
dist[nx][ny] = groupIdx;
check[nx][ny] = true;
q.push(make_pair(nx,ny));
}
}
}
group[z] = groupIdx;
groupIdx--;
z++;
}
int bfs2(int count){
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
int startValue;
//우선 섬의 좌표를 다 넣는다.
for(int i=0; i<a; i++){
for(int j=0; j<a; j++){
if(dist[i][j]== INF-count)
{
check2[i][j] = true;
q.push(make_pair(i,j));
startValue = dist[i][j];
}
}
}
int result =0;
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
//현재위치
int cx = q.front().first;
int cy = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
//다음위치
int nx = cx + dx[i];
int ny = cy + dy[i];
if(isInside(nx,ny))
{
//다른 그룹에 도달한 경우 반환
if(dist[nx][ny]>0 && dist[nx][ny]!= startValue)
{
return result;
}
//방문하지 않은 경우
else if (dist[nx][ny]==0 && !check2[nx][ny])
{
check2[nx][ny] = true;
q.push(make_pair(nx,ny));
}
}
}
}
result++;
}
return 9999;
}
int main(){
init();
cin >> a;
for(int i=0; i<a; i++){
for(int j=0; j<a; j++){
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
//그룹화 완료
for(int i=0; i<a; i++){
for(int j=0; j<a; j++){
if(map[i][j]==1 && dist[i][j]<=0)
{
bfs(i,j);
}
}
}
//새로 bfs
for(int i=0; i<z; i++){
//초기화
for(int j=0; j<a; j++){
for(int k=0; k<a; k++){
check2[j][k] = false;
}
}
//i = 그룹
Answer = min(Answer, bfs2(i));
}
if(Answer == 9999) cout << 0;
else cout << Answer << endl;
return 0;
}
tip: Flood fill
TIP
- vector, tuple, pair을 함수의 인자로 넘기면 복사본을 넘기므로 원본의 값이 변하지 않는다.
아래 함수를 실행하고 cout을 찍어도 1,1이 나옴.
ex)
void func1(pair<int, int>p){ p.first++; } int main(){ pair<int,int> p ={1,1}; func1(p) } - tie함수를 쓰면 쉽게 값을 뽑을 수 있다.
int x1,y1,z1, x2,y2,z2; tuple<int,int,int> a = {2,3,4} x1 = get<0>(t), y1 = get<1>(t), z1=get<2>(t); tie(x2,y2,z2); - 모든 경우의 수를 따져야 할때는 next_permutation()을 활용하자
인싸들의 가위바위보(16986)
회고
- 디버깅한다고 중간중간 시간을 많이 까먹었다 ㅎㅎ
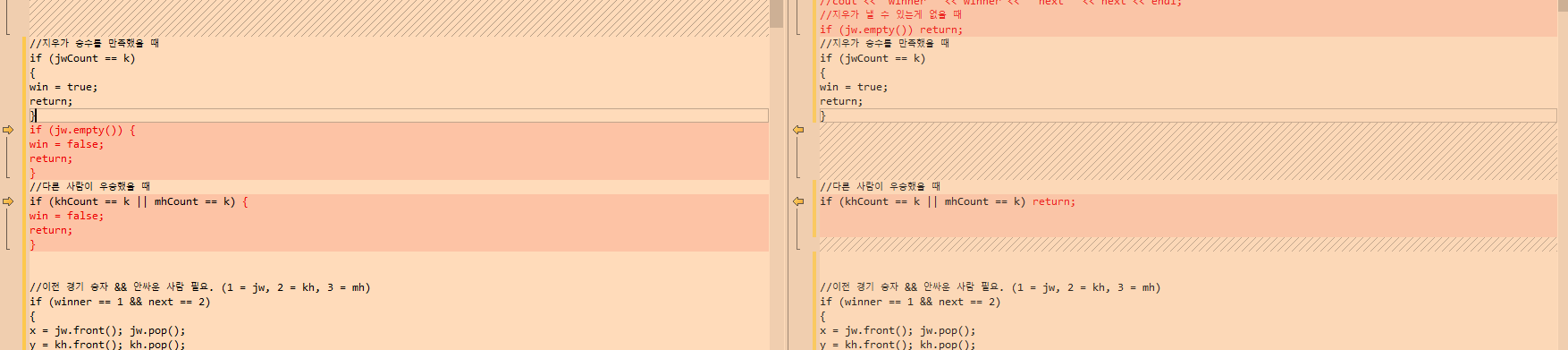
- 마지막 코드랑 차이를 비교할 것!
아래사진부분의 코드가 다른데… 테스트가 필요해보인다.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
int jwCount, khCount, mhCount;
//상성을 나타내는 표
int a[9][9];
bool win;
vector<int> jwTemp;
//경희, 민호의 순서
queue<int> jw;
queue<int> kh;
queue<int> mh;
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
a[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
//들어올 떄 우선순위를 정해서 들어갈 것
void fight(int winner, int next) {
//priority = true이면 무승부 시 winner가 이김
int x, y;
if (win) {
return;
}
else
{
//지우가 승수를 만족했을 때
if (jwCount == k)
{
win = true;
return;
}
if (jw.empty()) {
win = false;
return;
}
//다른 사람이 우승했을 때
if (khCount == k || mhCount == k) {
win = false;
return;
}
//이전 경기 승자 && 안싸운 사람 필요. (1 = jw, 2 = kh, 3 = mh)
if (winner == 1 && next == 2)
{
x = jw.front(); jw.pop();
y = kh.front(); kh.pop();
//x가 y를 이김 (jw승)
if (a[x][y] == 2)
{
jwCount++;
fight(1, 3);
}
else {
khCount++;
fight(2, 3);
}
}
else if (winner == 1 && next == 3)
{
x = jw.front(); jw.pop();
y = mh.front(); mh.pop();
//x가 y를 이김 (jw승)
if (a[x][y] == 2)
{
jwCount++;
fight(1, 2);
}
//비기든 지든 mh승
else {
mhCount++;
fight(3, 2);
}
}
else if (winner == 2 && next == 1)
{
x = kh.front(); kh.pop();
y = jw.front(); jw.pop();
//x가 y를 이김 (jw승)
if (a[x][y] == 0)
{
jwCount++;
fight(1, 3);
}
//비기든 이기든 kh승
else {
khCount++;
fight(2, 3);
}
}
else if (winner == 2 && next == 3)
{
x = kh.front(); kh.pop();
y = mh.front(); mh.pop();
//x가 y를 이김 (kh승)
if (a[x][y] == 2)
{
khCount++;
fight(2, 1);
}
//비기든 지든 mh승
else {
mhCount++;
fight(3, 1);
}
}
else if (winner == 3 && next == 1)
{
x = mh.front(); mh.pop();
y = jw.front(); jw.pop();
//y가 x 이김 (jw승)
if (a[x][y] == 0)
{
jwCount++;
fight(1, 2);
}
//비기든 이기든 mh승
else {
mhCount++;
fight(3, 2);
}
}
else if (winner == 3 && next == 2)
{
x = mh.front(); mh.pop();
y = kh.front(); kh.pop();
//y가 x 이김 (kh승)
if (a[x][y] == 0)
{
khCount++;
fight(2, 1);
}
//비기든 이기든 mh승
else {
mhCount++;
fight(3, 1);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
//정상 동작 확인 완료
init();
//상성입력
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
//경희 20개
queue<int> khTemp;
queue<int> mhTemp;
for (int a = 0; a < 20; a++) {
int temp;
cin >> temp;
kh.push(temp-1);
}
//민호 20개
for (int a = 0; a < 20; a++) {
int temp;
cin >> temp;
mh.push(temp-1);
}
khTemp = kh;
mhTemp = mh;
//지우 1~N 손동작
for (int a = 0; a < n; a++) {
jwTemp.push_back(a);
}
win = false;
//지우가 할 수 있는 손동작 조합을 1줄씩 던진다.
do {
//정상입력 확인
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
jw.push(jwTemp[i]);
//지우 순서 확인
//cout << "jw[" << i << "] = " << jwTemp[i] << " ";
}
mh = mhTemp;
kh = khTemp;
//cout << endl;
jwCount = 0;
khCount = 0;
mhCount = 0;
//지우, 경희로 시작 -> fight 안에서 끝내고와라.
fight(1, 2);
//지우 초기화
while (!jw.empty()) {
jw.pop();
}
} while (next_permutation(jwTemp.begin(), jwTemp.end()));
//3k-2 경기 후 누군가는 이긴다.
//지우가 모든 손동작을 다냈을 때 못이겼으면 0출력
//무승부 시 뒷사람이 이긴다.
//이긴사람 & 참여하지 않았던 사람이 다음경기를 진행한다.
cout << win;
}
댓글남기기